Project Finance Overview
We deliver project finance solutions on a world scale along with an inexorable commitment to make every client deal more profitable. Global Trade Funding provides the international project financing you need along with deal structuring advisory services that mitigate risk and aggressively protects your interests.
With more than two decades of senior underwriting experience at some of the world’s biggest banks, our directors give us unparalleled underwriting expertise coupled with the strength derived from having many of the world’s top lenders and financial institutions as strategic partners. From that foundation, we develop some of the most innovative project funding solutions in the world and source unique project funding alternatives through capital markets and lenders worldwide. We also enhance your project with the capabilities of a global funding team with a history of successfully funding some of the most challenging and complex international financing projects in the world.
Our expertise in delivering successful project financing packages and our innate ability to match the right project with the right lenders, architects, engineers, consultants, builders, developers and all of the professionals your project will need is uncanny. Doing it seamlessly and at the right time gives us all the tools we need to arrange and deliver extraordinary financial solutions for challenging, difficult-to-place loans and projects.
Sustainability in international project financing means delivering at the most difficult of times. By exploiting our strengths and core expertise in project finance we are often successful at placing project development loans for clients whose financing has been declined by other financiers and lenders. If your project has been turned down, we can help. We’ll pre-underwrite your project financing to see if we can successfully fund your project where others have failed. Submit a Request for Project Financing now and we’ll get your financing started today.
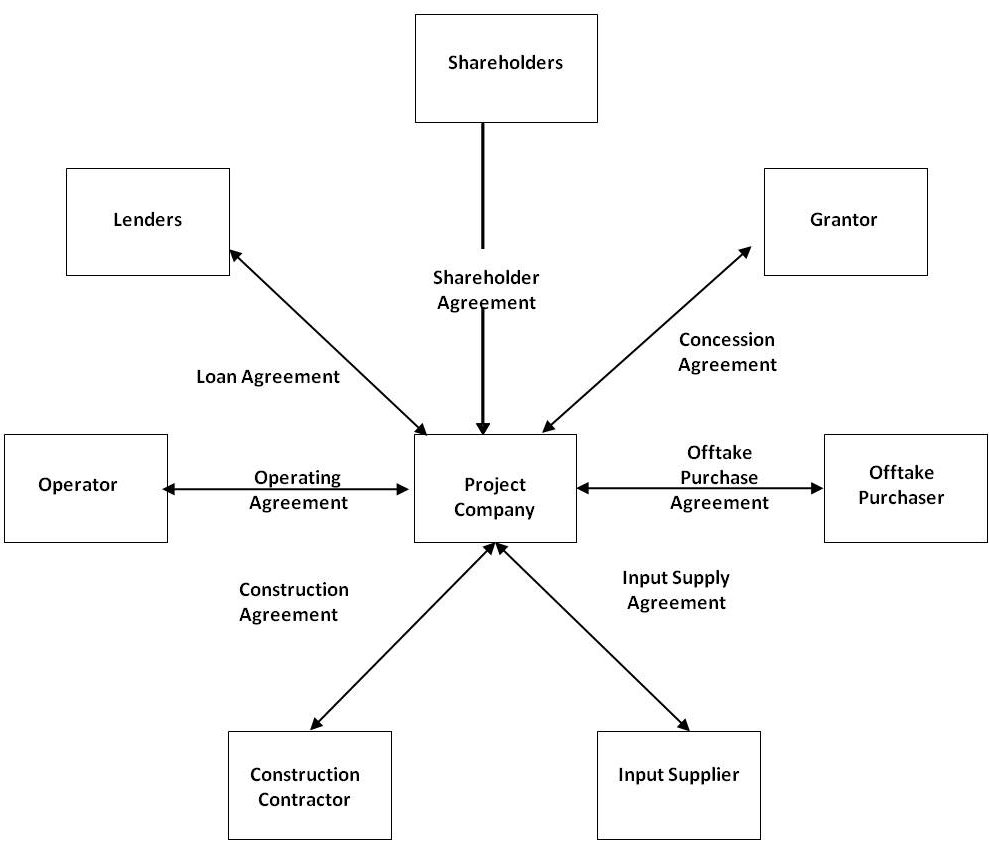
Project Finance Deal Structure
The typical project financing structure, which has been simplified for these purposes, for a build, operate and transfer (BOT) project is shown. The key elements of the structure are:
- Special Purpose Entity (SPE) project company with no previous business or record;
- Sole activity of project company is to carry out the project – it then subcontracts most aspects through construction contract and operations contract;
- For new build projects, there is no revenue stream during the construction phase and so debt service will only be possible once the project is online during the operations phase, thus there are significant risks during the construction phase;
- Sole revenue stream likely to be under an off-take or power purchase agreement;
- Project finance loans are non-recourse as to the borrowers, including the sponsors of the project and shareholders of the project company. There are extensive project financing documents that required no personal liability under the project loans. Thus, theProject Sponsor and project shareholders are liable only up to the extent of their shareholdings;
- Project Finance Structure means the project remains off balance sheet for the sponsors and for the host government.
Project finance is the lending structure that has financed a great many of the massive infrastructure and sovereign projects in emerging market countries throughout the world.
Project Finance Details
Project Finance provides long-term, limited recourse or non-recourse loans used to finance large commercial, industrial, infrastructure and sovereign projects in emerging market nations worldwide.
Unique to project financing is the debt and repayment structure are based on the projected cash flow of the project rather than the balance sheets of the project sponsor. Usually, a project finance structure involves a number of equity participants, who can be project sponsors or equity investors, and a consortium of lenders that provide loans to the project.
Project finance loans are almost always extended on a non-recourse or limited recourse basis and are secured by the project assets and operations. Repayment of the loans occurs entirely from project cash flow, not from the assets or credit of the borrower.
Underwriting for project development loans focuses on what is usually a business plan that includes extensive financial modeling and sensitivity analysis. The financing is typically secured by all of the project assets, including the revenue-generating components of the project. Lenders are granted a lien on all of the project assets and are further granted the right to assume managerial and operational control of a project, along with the mechanism to do so if the project doesn’t comply with the loan terms.
The borrower is typically a Special Purpose Entity or SPE which is created in the project documents specifically to own the project. The SPE ownership structure coupled with non-recourse debt effectively shields the assets of both the project sponsor and equity investors from collection efforts or deficiency actions if the project fails.
With collection actions barred if the deal fails, project lenders often require a commitment from the project owners to contribute capital to the project to ensure the project is sufficiently capitalized and financially sound, and also to demonstrate the project sponsors’ commitment to the deal.
Project finance is significantly more complex than traditional corporate finance or real estate lending. Historically international project finance has been used for mining, telecom, transportation and communication, water and electric utility distribution, and major public infrastructure projects.
Allocation of the risk stack among project participants is a key component of project finance. Project developments are often subject to technical, environmental, economic and political risks, particularly in developing countries and frontier and emerging markets. If the lenders or project sponsors determine that the risk exposure is too great during underwriting, the project is rendered unfinanceable.
Long-term contracts for construction, supply, off-take, operations and concessions, along with contracts establishing joint-ownership of the project are structured in extensive project documentation to best align the interests and incentives of all the project participants. They are also designed to dissuade bad behavior on the part of the deal participants. In this way, project risk is allocated amongst the deal participants who are best able to manage the risk.
The amounts involved in project development financing are often so vast that no single lender could or should provide the entirety of the project financing. Instead, the project financing is often syndicated to a consortium of lenders to distribute the risk.
Project financing was used as far back as the ancient Greeks and Romans to finance maritime voyages. It was project finance that funded construction of the Panama Canal and the North Sea oil wells.
Today, most project financing is deployed in developing countries around the world where the need for project financing remains high and will for the foreseeable future. As more countries move from frontier to emerging economies demand for public utilities and infrastructure will continue to increase.
Project Finance Expertise
Project Finance Modeling
Project Sponsorswho are seeking investors, lenders, or other stakeholders have to appeal to these potential project participants by presenting them with a proposal that is sufficiently compelling to get them to risk vast sums of money investing in their project. In other words, project sponsors must demonstrate that an investment in their project will provide a return on their invested capital that is great enough to put their money at risk.
Most proposed investments involve the acquisition of an asset that is already in operation and already has demonstrable revenue, such as a company, an apartment community or an industrial facility. Project financings don’t have operating assets with demonstrable because they involve the development of assets. With unproven revenue, expenses and cash flow, project sponsors must base their proposals to potential equity investors and lenders on projections. They do that with financial models and well-written, compelling business plans.
Project financial models are sophisticated computer spreadsheets that employ a lengthy list of business assumptions and variables to develop financial forecasts of capital costs, revenues, expenses, cash flow and future value of the assets. Financial models are tools used by project sponsors to negotiate with investors and lenders, and as support for appraisals and financial feasibility studies.
Because financial models form virtually the entire basis for investing in or lending on the proposed project, they must be based on reasonable, believable and transparent assumptions and variables that reflect the anticipated real-life interaction between data and calculated values. Financial models must be capable of sensitivity analysis that calculate projections based on a range of data variations. They must also demonstrate future profits and returns on investment which are sufficiently compelling to convince investors and lenders to invest in your project.
Project Finance was first used by an Italian merchant bank in 1299 to finance the development of English silver mines. England repaid the Italian bank entirely with the silver output from the mines.
Project Finance Learning Center
Project finance was first used in 1299 when an Italian merchant bank provided the project financing to finance the development of English silver mines. England repaid the Italian merchant bank who funded the project with the output from the mines. Project financing has been used to finance thousands of projects since those silver mines, including such notable projects as the Panama Canal and North Sea oil platforms. Our Project Finance Learning Center includes information we hope will improve understanding of this type of finance.
Definition of Project Finance
Project finance is not as well understood than it should be due largely to the fact that there is no consensus definition of project finance. Perceptions of what constitutes project financing vary depending on the definition of project finance you first learned. We list three of the most widely accepted definitions below.
A financing of a particular economic unit in which a lender is satisfied to look initially to the cash flow and earnings of that economic unit as the source of funds from which a loan will be repaid and to the assets of the economic unit as collateral for the loan.1
The raising of funds to finance an economically separable capital investment project in which the providers of the funds look primarily to the cash flow from the project as the source of funds to service their loans and provide the return of and a return on their equity invested in the project.2
The financing of long-term infrastructure, industrial projects and public services based upon a non-recourse or limited recourse financial structure where project debt and equity used to finance the project are paid back from the cash flow generated by the project.3
Project Finance Questions & Answers
Project Finance Lexicon
Accounts Receivable
Accounts Receivable is money owed to a company by a customer for products and /or services sold. Accounts receivable is considered a current asset on a balance sheet once an invoice has been sent to the customer.
Accounts Receivable Factoring
Accounts Receivable Factoring is a method of Trade Financing where a company sells their accounts receivable in exchange for working capital. The purchaser of the receivables relies on the creditworthiness of the customers who owe the invoices, not the subject company.
For details go to Accounts Receivable Factoring »
Advance Against Documents
Advances Against Documents are loans made solely based on the security of the documents covering the shipment.
Asset Based Lending
Asset Based Lending is a method of Trade Financing that allows a business to leverage company assets as collateral for a loan. Asset-based loans are an alternative to more traditional lending which is generally characterized as a higher risk which requires higher interest rates.
Cash Against Documents
Cash Against Documents is the payment for goods in which a commission house or other intermediary transfers title documents to the buyer upon payment in cash.
Cash in Advance
Payment for goods in which the price is paid in full before shipment is made. This method is usually used only for small purchases or when the goods are built to order.
Cash with Order
Cash with Order is the payment for goods whereby the buyer pays when ordering and in which the transaction is binding on both parties.
Commercial Finance
Commercial Finance is defined as the offering of loans to businesses by a bank or other lender. Commercial loans are either secured by business assets, accounts receivable, etc., or unsecured, in which case the lender relies on the borrower’s cash flow to repay the loan.
Confirmed Letter of Credit
A Confirmed Letter of Credit is a Letter of Credit issued by a foreign bank, which has been confirmed as valid by a domestic bank. An exporter whose form of payment is a Confirmed Letter of Credit is assured of payment by the domestic bank who confirmed the Letter of Credit even if the foreign buyer or the foreign bank defaults.
Consignment
Consignment is a delivery of merchandise from an exporter (the consignor) to an agent (the consignee) subject to an agreement by the agent that the agent will sell the merchandise for the benefit of the exporter, subject to certain limitations, like a minimum price. The exporter (consignor) retains ownership of and title to the goods until the agent (consignee) has sold them. Upon the sale of the goods, the agent typically retains a commission and remits the remaining net proceeds to the exporter.
For details go to Consignment Purchase »
Cross-Border Sale
A Cross-Border Sale refers to any sale that is made between a firm in one country and a firm located in a different country.
Factoring
Factoring is the selling of a company’s invoices and accounts receivable at a discount. The lender assumes the credit risk of the debtor and receives the cash when the debtor settles the account.
For details go to Accounts Receivable Factoring »
Invoice Discounting
Invoice Discounting is a type of loan that is drawn against a company’s outstanding invoices but does not require that the company give up administrative control of those invoices.
factoring invoices
factoring invoices is one of the most common methods of trade financing. Your company sells their invoices to a factor in exchange for immediate liquidity. The factor who purchases the invoices relies on the creditworthiness of the customers who owe the invoices, not the subject company.
For details go to factoring invoices »
Irrevocable Letter of Credit
Irrevocable Letter of Credit is a Letter of Credit in which the specified payment is guaranteed by the bank if all terms and conditions are met by the drawee.
Letter of Credit
Letter of Credit or LC is the most common trade finance solution in the world. A Letter of Credit is a document issued by a bank for the benefit of a seller or exporter, which authorizes the seller to draw a specified amount of money, under specified terms, usually the receipt by the issuing bank of certain documents within a given time.
For details go to Letters of Credit For Imports »
Open Account
Open Account is a trade arrangement in which goods are shipped to a foreign buyer without guarantee of payment. The obvious risk this method poses to the supplier makes it essential that the buyer’s integrity be unquestionable.
For details go to Open Accounts »
Pro forma Invoice
Pro forma Invoice is an invoice provided by a supplier prior to the shipment of merchandise, which informs the buyer of the kinds, nature and quantities of goods to be shipped along with their value, and other important specifications such as weight and size.
Receivable Management
Receivable Management involves processing activities related to managing a company’s accounts receivable including collections, credit policies and minimizing any risk that threatens a firm from collecting receivables.
Revocable Letter of Credit
Revocable Letter of Credit is a Letter of Credit that can be canceled or altered by a buyer after it has been issued by the buyer’s bank.
Structured Trade Finance
Structured Trade Finance is cross-border trade finance in emerging markets where the intention is that the loan gets repaid by the liquidation of a flow of commodities.
Trade Credit Insurance
Trade Credit Insurance is a risk management product offered to business entities wishing to protect their balance sheet assets from loss due to credit risks such as protracted default, insolvency, and bankruptcy. Trade Credit Insurance often includes a component of political risk insurance, which ensures the risk of non-payment by foreign buyers due to currency issues, political unrest, expropriation, etc.
Project Finance Documents
› EPC Contract
› O&M Agreement
› Loan Agreement
› Offtake Agreement
› Supply Agreement
› Intercreditor Agreement
› Tripartite Deed
› Common Terms Agreement
› Concession Deeds
› Shareholder Agreement
Project Finance Participants & Stakeholders
Get Financing For Your Project Today
Unparalleled underwriting expertise uniquely positions us to identify financing obstacles and improve deal structure to minimize risk and attract lenders. Then we present an optimized loan package to our worldwide network of lenders and investors resulting in project finance with the best terms and least risk in the industry.
Dublin · Hong Kong · London · Mexico City · Prague · Sydney · Vancouver · Washington DC · Zurich